How to Manufacture LED Lights?
LED lights have revolutionized the world of lighting, offering energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility in a variety of applications. Whether it’s in our homes, offices, or even outdoor spaces, LED lights have become an integral part of modern lighting solutions. But have you ever wondered how to manufacture LED lights?
Throughout this LED lighting guide, we will explore various aspects of LED light manufacturing, including the production of LED chips, the assembly of components, quality control measures, and the packaging and distribution process.
Let’s shed some light on how these extraordinary devices are made.
What are the Basic Components of LEDs?
LEDs consist of several basic components that work in harmony to produce light efficiently and effectively. Understanding these components is essential to grasp the fundamental workings of an LED and its manufacturing process.
Semiconductor Chip
At the heart of an LED lies a semiconductor chip, usually made of materials such as gallium nitride (GaN) or gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP). The chip is responsible for generating light when an electric current passes through it. The specific composition of the semiconductor determines the color of the emitted light.
Substrate
The substrate acts as a support for the semiconductor chip. It is typically made of materials like sapphire or silicon carbide, providing stability and durability to the LED.
Contacts
LEDs have two electrical contacts—an anode and a cathode. The anode, usually the longer lead or the positive terminal, connects to the p-type (+) region of the semiconductor. The cathode, typically the shorter lead or the negative terminal, connects to the n-type (-) region of the semiconductor.
Encapsulation
To protect the delicate semiconductor chip and enhance the efficiency of light emission, LEDs are encapsulated within a transparent or translucent material. This encapsulation material can be an epoxy resin or a silicone-based compound. It helps to focus and direct the emitted light, ensuring optimal brightness and distribution.
Reflective Cavity
Some LEDs incorporate a reflective cavity or a cup-like structure behind the semiconductor chip. This cavity helps redirect the emitted light toward the desired direction, increasing the overall efficiency of the LED.
Wire Bonds
Wire bonds are used to establish electrical connections between the contacts of the LED and the semiconductor chip. Typically, thin gold or aluminum wires are bonded to the contacts, ensuring a reliable electrical connection.
Must read: Different Types of LED Strip Lights and Their Features
LED Lights Manufacturing Process: How LED Lights Are Made?

Pre-Production Phase
Before the manufacturing of LED lights can commence, a crucial pre-production phase takes place, encompassing essential tasks that lay the foundation for a successful production process. This phase involves research and development, designing the LED lights, and carefully selecting the necessary components and materials.
Research and Development:
During the research and development stage, manufacturers explore new technologies, conduct experiments, and analyze market trends to identify opportunities for innovation. This phase allows for the refinement of existing LED designs or the creation of entirely new concepts, ensuring that the final product aligns with industry advancements and consumer demands.
Designing the LED Lights:
Designing LED lights involves a combination of creativity, engineering expertise, and attention to detail. Manufacturers consider factors such as the desired lighting output, form factor, heat dissipation capabilities, and energy efficiency.
This stage includes designing the layout of the LED chips, determining the optimal arrangement of components on the printed circuit board (PCB), and creating a visually appealing and functional product design.
Selecting Components and Materials:
Careful selection of components and materials is crucial for achieving the desired performance and reliability of LED lights. This involves sourcing high-quality LED chips, selecting appropriate substrates for the PCB, choosing reliable electrical contacts and wire bonds, and deciding on the encapsulation material that will protect the LED components.
Also read: Simple Way To Connect Multiple LED Lights To One Power Source
LED Chip Manufacturing
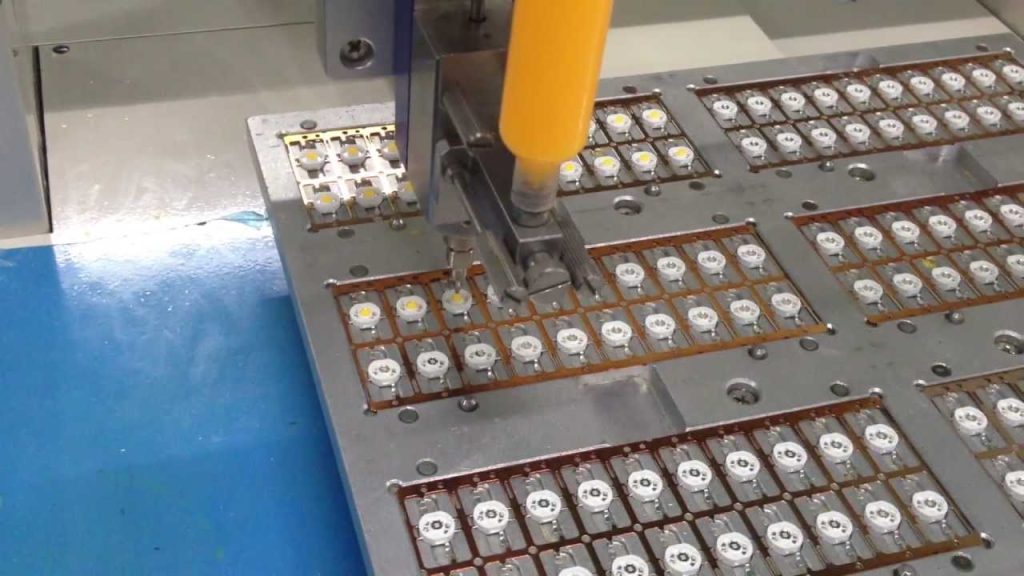

LED chips serve as the core components responsible for emitting light in LED lights. The manufacturing process of LED chips involves several intricate steps that require precision and expertise. Let’s explore the key stages involved in LED chip manufacturing:
Wafer Fabrication
The process begins with the fabrication of a wafer, typically made of a semiconductor material like gallium nitride (GaN). This involves the growth of a thin crystalline layer on a substrate through techniques such as metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). The choice of substrate and growth parameters significantly impact the performance and efficiency of the LED chips.
Epitaxy Process
During epitaxy, additional layers are grown on the wafer to create the active region where light emission occurs. This is achieved through epitaxial deposition methods, such as molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) or metal-organic vapor phase epitaxy (MOVPE). The epitaxial layers consist of different semiconductor materials, including n-type and p-type layers that form a junction for efficient electron-hole recombination.
Dicing and Packaging
After the epitaxy process, the wafer is diced into individual LED chips. Precision cutting techniques, such as laser scribing or mechanical sawing, are employed to separate the chips while minimizing waste. Once diced, the LED chips undergo a packaging process to protect them and facilitate electrical connections. This includes attaching electrical contacts, such as gold or aluminum wire bonds, to the appropriate regions of the LED chip.
LED Light Assembly
The assembly of LED lights involves bringing together various components to create a fully functional lighting device. This process requires meticulous attention to detail and careful execution to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and aesthetics. Let’s explore the key steps involved in the assembly of LED lights:
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Manufacturing
The assembly process begins with the fabrication of the PCB, which serves as the foundation for mounting and connecting the LED chips and other electronic components. The PCB is typically made of non-conductive material like fiberglass or ceramic, with copper traces etched onto it to provide electrical pathways.
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) Assembly Process
Surface Mount Technology is commonly used in LED light assembly, allowing for the precise placement and soldering of components onto the PCB. Automated equipment is utilized to accurately position and solder surface-mount LED chips, resistors, capacitors, and other electronic components onto the PCB. This process ensures secure electrical connections and efficient use of space on the board.
Soldering and Connection of Components
Soldering plays a crucial role in securely connecting the LED chips, electrical contacts, and other components to the PCB. This is typically done using reflow soldering techniques, where solder paste is applied to the PCB, and the entire assembly is heated to melt the solder and create reliable connections.
Optical Components and Lens Installation
To control and distribute the emitted light, optical components and lenses are integrated into the LED light assembly. These components help shape the light beam, enhance efficiency, and achieve desired lighting characteristics. Lenses may be added to focus or diffuse the light, depending on the specific application requirements.
Also read: How to Stop Dimmable LED Flash and Flickering
Quality Control and Testing
One crucial aspect of quality control and testing is electrical performance evaluation. This involves conducting tests to assess the forward voltage, current-voltage characteristics, and electrical continuity of the LED lights.
In addition to electrical testing, light output, and color quality are also assessed. Luminous intensity, color temperature, and color rendering index (CRI) are measured to determine the brightness and color accuracy of the LED lights. This step ensures that the lights meet the desired specifications and provide consistent and visually appealing illumination.
Quality control and testing for LED lights are not limited to the manufacturing phase alone. Random sample testing and inspections may also be conducted during the post-production stage to verify the ongoing quality and consistency of the LED lights.
Environmental Considerations

LED manufacturers take into account various environmental considerations throughout the manufacturing process to minimize their ecological footprint and promote sustainability. Let’s explore some of these key environmental considerations:
- LED lights are renowned for their energy efficiency, consuming significantly less electricity than traditional incandescent or fluorescent lights. By manufacturing LED lights that require lower power consumption, manufacturers contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing the overall demand for electricity.
- LED lights are designed to be free from hazardous substances like mercury, which are commonly found in traditional lighting technologies. LED manufacturers adhere to regulations and guidelines such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) to ensure the absence of harmful materials in their products. This reduces the environmental impact during production, usage, and end-of-life disposal.
- LED lights have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lights, resulting in reduced waste generation and fewer replacements. Manufacturers focus on producing LED lights with high-quality components and robust designs to enhance durability and minimize the need for frequent replacements, thereby reducing waste and resource consumption.
- LED manufacturers encourage the proper recycling and disposal of LED lights at the end of their lifespan. LEDs can contain valuable materials such as aluminum, copper, and rare earth elements that can be extracted and reused. Proper recycling practices help minimize environmental pollution and conserve valuable resources.
- LED manufacturers strive to implement sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes optimizing energy usage in production facilities, minimizing water consumption, reducing waste generation, and promoting the use of eco-friendly materials and packaging.
You may also like: Should You Switch From CFL To LED Light Bulb?
Final Words
In conclusion, the manufacturing process of LED lights is intricate and requires a sophisticated blend of technology, precision engineering, and quality control to ensure that the final products meet the necessary standards of efficiency and durability. Starting with the creation of the LED itself, the process involves semiconductor wafer fabrication where layers of materials such as gallium arsenide or gallium nitride are deposited. These materials are critical because they determine the color and efficiency of the LED. The wafers are then cut into very small pieces, each becoming an individual LED. This step is followed by the mounting of these diodes on heat sinks to manage heat dissipation, a vital aspect since overheating can significantly reduce the lifespan and performance of LEDs.
Furthermore, the assembly process involves soldering these diodes onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) and integrating them with other electronic components like resistors and capacitors that help regulate the power flow. Each unit then undergoes rigorous testing to check for electrical functionality, color consistency, and luminosity. Quality control at every stage of assembly ensures that any defects are identified and rectified early in the production process. Finally, the LEDs are encased in durable, light-enhancing lenses and assembled into their final housing, which varies depending on their intended use — from industrial lighting fixtures to residential light bulbs. The ability to efficiently scale these processes while maintaining high standards of quality is crucial for LED manufacturers to meet the growing global demand for these energy-efficient lighting solutions. This manufacturing complexity reflects the sophistication of LED technology, which is continually advancing to provide brighter, more durable, and increasingly efficient lighting options.
So, the next time you switch on an LED light and enjoy its efficient and vibrant illumination, remember the journey it has taken from the research labs to the assembly lines, embodying the ingenuity of human innovation and the commitment to a brighter, greener future.






