What Does LED Density on an LED Strip Mean?
Have you ever wondered what LED density on an LED strip means? Maybe your TV won’t turn on, or your Christmas lights are flickering. If so, you’re not alone. LED density is a common problem that can cause all sorts of issues.
In this article, I’ll explain what LED density is and how it can affect your lights. I’ll also share some tips on how to troubleshoot LED density problems. So if you’re having trouble with your LED lights, read on!
By the end of this article, you’ll better understand LED density and how to fix it. So if you’re ready to learn more, let’s get started!
What Does LED Density on an LED Strip Mean?
LED density is a measure of the number of LEDs per unit length of an LED strip. It is typically expressed in LEDs per meter (LEDs/m). The higher the LED density, the more LEDs there are per unit length, and the brighter the strip will be.
LED density is an important factor to consider when choosing an LED strip for your project. If you need a bright, uniform light, then you will want to choose an LED strip with a high LED density. However, if you are working with a tight budget, you may want to choose an LED strip with a lower LED density.
LED density is also affected by the size of the LEDs. Smaller LEDs can be packed closer together than larger LEDs, so an LED strip with small LEDs can have a higher LED density than an LED strip with large LEDs.
In addition to the number of LEDs per unit length, LED density also refers to the distribution of the LEDs along the strip. Some LED strips have LEDs evenly spaced along the strip, while others have LEDs clustered together in certain areas. The distribution of the LEDs can affect the overall appearance of the light.
Also read: RGBWW vs RGBW Strip Lights: Which Is Right for You?
How to Calculate LED Density?

The formula for calculating LED density is:
“`
LED density (LEDs/m) = Number of LEDs / Length of strip (m)
“`
For example, if an LED strip has 100 LEDs and is 1 meter long, then the LED density is 100 LEDs / 1 m = 100 LEDs/m.
Factors Affecting LED Density
Several factors can affect LED density, including:
- The size of the LEDs: Smaller LEDs can be packed closer together than larger LEDs, so an LED strip with small LEDs can have a higher LED density than an LED strip with large LEDs.
- The spacing of the LEDs: Some LED strips have LEDs evenly spaced along the strip, while others have LEDs clustered together in certain areas. The distribution of the LEDs can affect the overall appearance of the light.
- The type of LED strip: There are two main types: flexible LED strips and rigid LED strips. Flexible LED strips are more flexible than rigid LED strips, but they typically have a lower LED density. Rigid LED strips are less flexible than flexible LED strips, but they typically have a higher LED density.
Also read: 2835 vs 3528 vs 5050: Understanding LED Light Strip
Choosing the Right LED Density for Your Project
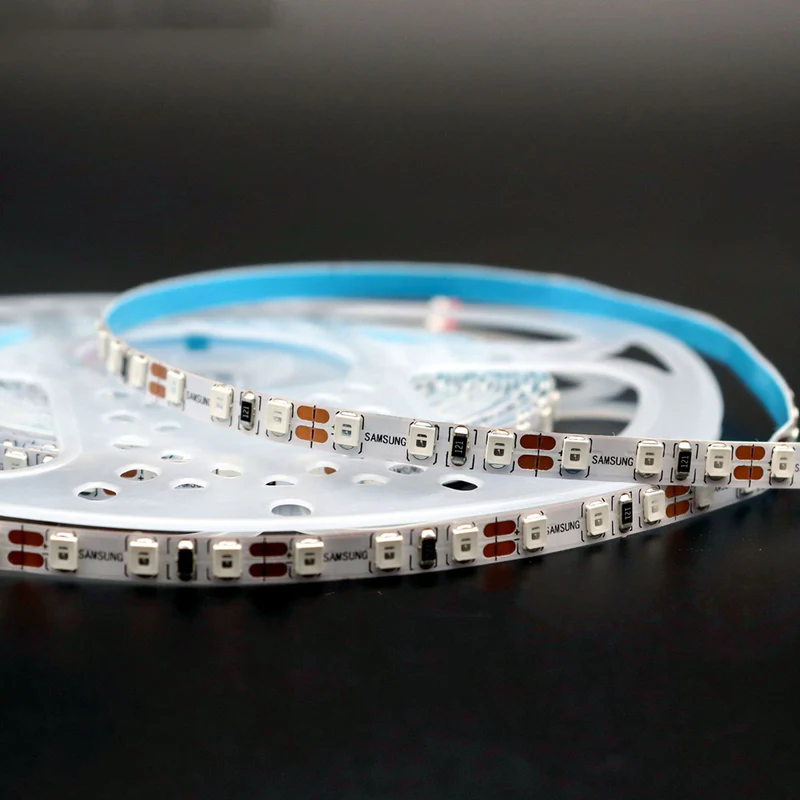

The right LED density for your project will depend on some factors, including:
- Brightness of the light: The higher the LED density, the brighter the light will be.
- Size of the project: The larger the project, the more LEDs you will need.
- Budget: The higher the LED density, the more expensive the LED strip will be.
FAQs
What is the difference between high and low LED density strips?
High LED density strips have more LEDs per meter than low LED density strips. This means that they are brighter and produce a more uniform light. However, they are also more expensive than low LED-density strips.
What are the benefits of using a high LED density strip?
High LED density strips offer a number of benefits over low LED density strips, including:
- Brightness: High LED density strips are brighter than low LED density strips. This makes them ideal for applications where brightness is important, such as under cabinet lighting and accent lighting.
- Uniformity: High LED density strips produce a more uniform light than low LED density strips. This means that there is less variation in brightness from one end of the strip to the other.
- Cost-effectiveness: High LED density strips are more cost-effective than low LED density strips. This is because they use fewer LEDs to achieve the same level of brightness.
What are the drawbacks of using a high LED density strip?
The main drawback of using a high LED density strip is the cost. High LED density strips are more expensive than low LED density strips. This is because they use more LEDs to achieve the same level of brightness.
What factors should I consider when choosing an LED strip?
When choosing an LED strip, there are some factors you should consider, including:
- LED density: The LED density of the strip will determine how bright the strip is.
- Power rating: The power rating of the strip will determine how much power it consumes.
- Type of lens: The type of lens used on the strip will affect the distribution of light.
- Price: The price of the strip will vary depending on the LED density, power rating, and lens type.
By considering these factors, you can choose an LED strip that meets your needs and budget.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of LED density in LED strip lighting is critical for users to understand as it significantly impacts both the aesthetic and functional aspects of lighting. LED density, defined as the number of LEDs per meter or foot, determines the brightness and consistency of the light emitted from the strip. Higher densities generally result in brighter and more uniformly distributed light, which is essential for tasks requiring precision and clarity, such as under cabinet lighting in kitchens or workspace illumination. Conversely, lower densities might be suitable for ambient lighting or decorative purposes where a softer light is preferable. The choice of LED density should align with the specific lighting needs of the area to be illuminated, balancing between energy consumption, brightness requirements, and the desired visual effect.
Moreover, it’s important for consumers to consider the implications of higher LED densities beyond just improved light output. Higher densities can lead to increased power consumption and heat generation, necessitating careful consideration of heat management and power supply solutions. Efficient heat dissipation is vital to preserve the lifespan of the LEDs, as excessive heat can degrade the diodes over time and reduce their operational efficiency. Furthermore, when planning the installation of high-density LED strips, one must ensure that the power supply is adequately rated to handle the increased load. By comprehensively understanding LED density and its effects on lighting performance and system requirements, users can make informed decisions that enhance both the environment and the longevity of their LED lighting solutions.






